Meylan-Perentes lab
At AGORA, Meylan and Perentes and their groups have now joined forces, to prioritize translational research projects on thoracic malignancies with a clear clinical perspective. Together, we are studying how the efficacy of local or systemic cancer treatments could be improved through the activation of innate and adaptive immunity. We hope that our detailed mechanistic studies, obtained from complementary models and experimental approaches, will provide insights that will lead to new opportunities for clinical targeting. ...
Research projects
The immunometabolic response of thoracic malignancies
We are exploring the immune ecosystem of thoracic malignancies, during tumor growth and in response to treatment. Our structure results from an outstanding union of two complementary research laboratories, the Meylan and Perentes groups, who combine expertise in immuno-oncology and translational science. Together, we seek to elucidate key molecular and immune-mediated mechanisms that dictate disease progression and therapeutic response with in-depth investigations from mouse models and clinical patient samples. Our ultimate goal is to push the current boundaries of knowledge and pave the way for innovative therapeutic strategies that will improve the efficacy of current treatments and patient outcomes.
From our recently published and unpublished findings, we are developing two principal research axes:
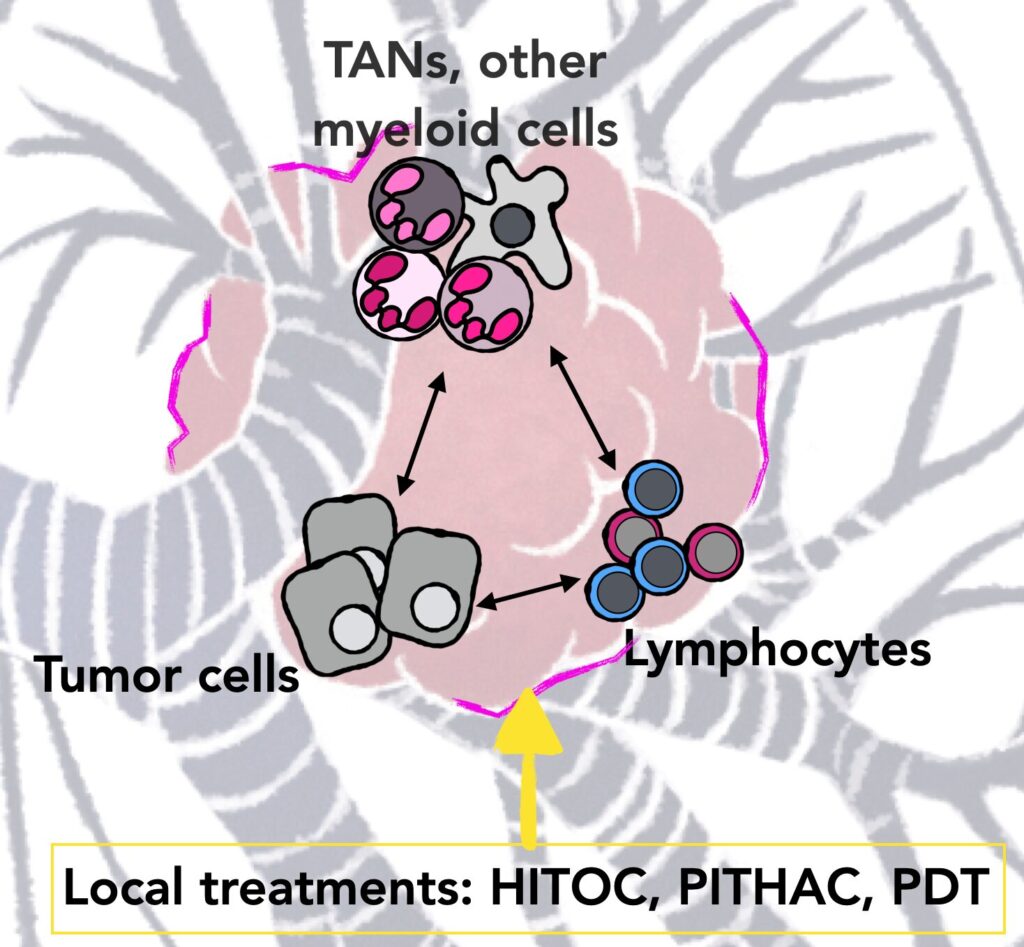
1) Therapy-mediated immune response in pleural carcinosis.
Locoregional therapies such as photodynamic therapy (PDT) and hyperthermic intrathoracic chemotherapy (HITOC) have shown promising response in pleural cancers. Initially developed to eliminate residual tumor cells following cytoreductive surgery, their immunomodulatory effects have received comparatively little attention until recently.
In murine models of pleural carcinosis, we identified that both approaches could profoundly reshape the tumor-associated immune signature and promote response to immune checkpoint blockade (CIR 2025 ; JITC 2025). From our initial preclinical findings, a phase I clinical trial has been initiated in patients with pleural carcinosis, for evaluation of pressurized intrathoracic aerosol cisplatin (PITHAC) administration. Based on our discoveries, we want now to decipher the mechanisms underlying the initiation of an effective anti-tumor immune control, and how they could be harnessed for an optimal response to existing immunotherapies.
2) Perturbations and functions of neutrophils.
Long overlooked in the field of cancer, neutrophils, their complex regulations, and their functions have recently begun to emerge. In non-small cell lung cancer, we demonstrated that neutrophils are altered upon tumor homing, with tumor-associated neutrophils (TAN) exhibiting increased glycolytic metabolism and survival capacity, two key parameters that contribute to their tumor support (CanRes 2021 ; EMBOMM 2024). Now we want to interrogate more globally, but also in greater detail, the metabolic and functional disturbances of neutrophils during cancer progression to advanced stage, including in pleural carcinosis, and during response to local or systemic treatments. We hope our findings will help identify new vulnerabilities of tumor-supporting neutrophils that can be exploited clinically.
Latest publications
Post-operative volume changes in residual lung lobes after VATS pulmonary segmentectomy for early stage non-small cell lung cancer.
Dewarrat A, Troxler R, Abdelnour E, (...), Perentes JY, Krueger T, Gonzalez M
Journal of cardiothoracic surgery – 2026 Feb 5
Real-world outcomes of stage III NSCLCs managed by surgery or definitive radiation therapy in the era of immunotherapy.
Abdelnour-Berchtold E, Chriqui LE, Zermatten L, (...), Peters S, Bouchaab H, Perentes JY
European journal of surgical oncology : the journal of the European Society of Surgical Oncology and the British Association of Surgical Oncology – 2026 Jan 10
Outcomes After VATS Single Versus Multiple Segmentectomy for cT1N0 Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer.
Tian Y, Zanfrini E, Abdelnour-Berchtold E, (...), Perentes JY, Krueger T, Gonzalez M
Cancers – 2025 Nov 28
Low-dose photodynamic therapy promotes vascular E-selectin expression in chest malignancies, improving immune infiltration and tumor control.
Chriqui LE, Marie DN, Sifis A, (...), Joyce J, Cavin S, Perentes JY
Journal for immunotherapy of cancer – 2025 Jun 10
Hyperthermic Intrathoracic Chemotherapy Modulates the Immune Microenvironment of Pleural Mesothelioma and Improves the Impact of Dual Immune Checkpoint Inhibition.
Hao Y, Gkasti A, Managh AJ, (...), Dyson PJ, Cavin S, Perentes JY
Cancer immunology research – 2025 Feb 3
Bcl-xL targeting eliminates ageing tumor-promoting neutrophils and inhibits lung tumor growth.
Bodac A, Mayet A, Rana S, (...), Demetter P, Radtke F, Meylan E
EMBO molecular medicine – 2023 Dec 20
GLUT1 Expression in Tumor-Associated Neutrophils Promotes Lung Cancer Growth and Resistance to Radiotherapy.
Ancey PB, Contat C, Boivin G, (...), Rathmell JC, Vozenin MC, Meylan E
Cancer research – 2021 Mar 22
Team

Meylan-Perentes lab
Principal investigators

Etienne Meylan
Associate Professor, PhD, Co-Director of the Thoracic Cancer Translational Research Laboratory, Division of Thoracic Surgery, CHUV

Jean Yannis Perentes
Professor, MD-PhD, Head Physician, Co-Director of the Thoracic Cancer Translational Research Laboratory, Division of Thoracic Surgery, CHUV
Other members
Selected Publications
Low-dose photodynamic therapy promotes vascular E-selectin expression in chest malignancies, improving immune infiltration and tumor control.
Chriqui LE, Marie DN, Sifis A, (...), Joyce J, Cavin S, Perentes JY
Journal for immunotherapy of cancer – 2025 Jun 10
Hyperthermic Intrathoracic Chemotherapy Modulates the Immune Microenvironment of Pleural Mesothelioma and Improves the Impact of Dual Immune Checkpoint Inhibition.
Hao Y, Gkasti A, Managh AJ, (...), Dyson PJ, Cavin S, Perentes JY
Cancer immunology research – 2025 Feb 3
Phase I clinical trial testing the dose escalation and expansion of Pressurized IntraThoracic Hyperthermic Aerosol Cisplatin administration (PITHAC) for the management of pleural carcinosis.
Chriqui LE, Abdelnour-Berchtold E, Zanfrini E, (...), Peters S, Cavin S, Perentes JY
Cancer treatment and research communications – 2024 Dec 17
Bcl-xL targeting eliminates ageing tumor-promoting neutrophils and inhibits lung tumor growth.
Bodac A, Mayet A, Rana S, (...), Demetter P, Radtke F, Meylan E
EMBO molecular medicine – 2023 Dec 20
Neutrophil phenotypes and functions in cancer: A consensus statement.
Quail DF, Amulic B, Aziz M, (...), de Visser KE, Egeblad M, Kubes P
The Journal of experimental medicine – 2022 May 6
GLUT1 Expression in Tumor-Associated Neutrophils Promotes Lung Cancer Growth and Resistance to Radiotherapy.
Ancey PB, Contat C, Boivin G, (...), Rathmell JC, Vozenin MC, Meylan E
Cancer research – 2021 Mar 22
Low-dose photodynamic therapy promotes a cytotoxic immunological response in a murine model of pleural mesothelioma.
Cavin S, Gkasti A, Faget J, (...), Dyson PJ, Meylan E, Perentes JY
European journal of cardio-thoracic surgery : official journal of the European Association for Cardio-thoracic Surgery – 2020 Oct 1
Combined deletion of Glut1 and Glut3 impairs lung adenocarcinoma growth.
Contat C, Ancey PB, Zangger N, (...), Abel ED, Meibom A, Meylan E
eLife – 2020 Jun 23
Durable and controlled depletion of neutrophils in mice.
Boivin G, Faget J, Ancey PB, (...), Pittet MJ, Gunzer M, Meylan E
Nature communications – 2020 Jun 2
Neutrophils and Snail Orchestrate the Establishment of a Pro-tumor Microenvironment in Lung Cancer.
Faget J, Groeneveld S, Boivin G, (...), Piersigilli A, Xenarios I, Meylan E
Cell reports – 2017 Dec 12
RANKL Signaling Sustains Primary Tumor Growth in Genetically Engineered Mouse Models of Lung Adenocarcinoma.
Faget J, Contat C, Zangger N, Peters S, Meylan E
Journal of thoracic oncology : official publication of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer – 2017 Dec 6
Mutant CTNNB1 and histological heterogeneity define metabolic subtypes of hepatoblastoma.
Crippa S, Ancey PB, Vazquez J, (...), Delorenzi M, Michielin O, Meylan E
EMBO molecular medicine – 2017 Nov
GLUT3 is induced during epithelial-mesenchymal transition and promotes tumor cell proliferation in non-small cell lung cancer.
Masin M, Vazquez J, Rossi S, (...), Moradpour D, Oliver TG, Meylan E
Cancer & metabolism – 2014 Jul 29
Requirement for NF-kappaB signalling in a mouse model of lung adenocarcinoma.
Meylan E, Dooley AL, Feldser DM, (...), Turk E, Ouyang C, Jacks T
Nature – 2009 Oct 21
Cardif is an adaptor protein in the RIG-I antiviral pathway and is targeted by hepatitis C virus.
Meylan E, Curran J, Hofmann K, (...), Binder M, Bartenschlager R, Tschopp J
Nature – 2005 Sep 21
Related news
Events

Symposium on Translational Cancer Research | March 9th
Events

PhD Thesis Defense | October 24th
Events
AGORA Tumor Microenvironment Journal Club
Events
🌱 Second AGORA Sustainability Day | May 21st
Events
Oncology Grand Rounds, Prof. Jean Yannis Perentes and Prof. Etienne Meylan | May 16th
Events

Inaugural lecture, Prof. Jean Yannis Perentes | February 10th
Events












