Gfeller lab
Tumors form highly complex structures comprising many different cell types like cancer and immune cells. In our research, we use and develop computational biology and immuno-informatics to better understand and predict the interactions between immune and cancer cells. Our lab is affiliated to the Department of Oncology at the University of Lausanne (UNIL), the Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research (LICR) and the Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics (SIB). ...
Research projects
Analysis and predictions of antigen presentation and TCR recognition
The diversity of T-cell epitopes in cancer is overwhelming due the heterogeneity of genetic alterations and the polymorphism of HLA genes. To narrow down the most promising candidates, our lab has developed state-of-the-art predictors of HLA-I [Gfeller et al. J Immunol 2018, Gfeller et al. Cell Systems 2023] and HLA-II ligands [Racle et al. Nature Biotech 2019, Racle et al. Immunity 2023], as well as predictors of neo-epitope TCR recognition [Schmidt et al. Cell Rep Med 2021, Gfeller et al. Cell Systems 2023]. These predictions are largely based on high-quality HLA peptidomics data and machine learning algorithms for motif deconvolution [Bassani-Sternberg and Gfeller J Immunol 2016 , Racle et al. Nature Biotech 2019 ]. Our findings also revealed alternative binding modes of HLA ligands [Guillaume et al. PNAS 2018, Racle et al. Immunity 2023], and enabled us to better understand the properties of the antigen presentation pathways.
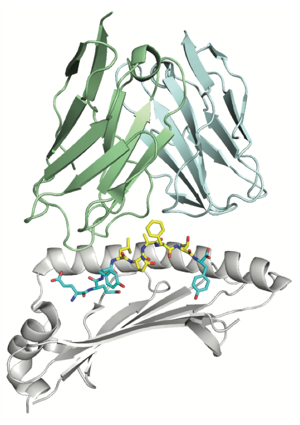
Modelling TCR repertoire and specificity
T cells have the ability to generate billions of T-Cell Receptors (TCRs) that can recognize various epitopes displayed on HLA molecules. While information about the presence of specific T cells in a tumor can be obtained with TCR-sequencing technologies, a major challenge remains to know which T cells recognize which epitopes. Together with several experimental collaborators, we are developing machine learning algorithms both for understanding and modelling the properties of the TCR repertoire and unraveling the determinants of TCR specificity for their cognate epitopes.
Latest publications
Building and analyzing metacells in single-cell genomics data.
Bilous M, Hérault L, Gabriel AA, Teleman M, Gfeller D
Molecular systems biology – 2024 May 29
Joint host-pathogen genomic analysis identifies hepatitis B virus mutations associated with human NTCP and HLA class I variation.
Xu ZM, Gnouamozi GE, Rüeger S, (...), Gfeller D, Urban S, Fellay J
American journal of human genetics – 2024 May 7
Deep learning predictions of TCR-epitope interactions reveal epitope-specific chains in dual alpha T cells.
Croce G, Bobisse S, Moreno DL, (...), Guillame P, Harari A, Gfeller D
Nature communications – 2024 Apr 13
Semi-supervised integration of single-cell transcriptomics data.
Andreatta M, Hérault L, Gueguen P, (...), Gfeller D, Berenstein AJ, Carmona SJ
Nature communications – 2024 Jan 29
Contemplating immunopeptidomes to better predict them
Gfeller D, Liu Y, Racle J
Seminars in Immunology – 2023 Mar 1
Both APRIL and antibody-fragment-based CAR T cells for myeloma induce BCMA downmodulation by trogocytosis and internalization.
Camviel N, Wolf B, Croce G, (...), Gfeller D, Zoete V, Arber C
Journal for immunotherapy of cancer – 2022 Nov 3
Team

David Gfeller
PhD Computational cancer biology, Associate Professor, Department of Oncology UNIL & CHUV, Ludwig adjunct scientist, Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research Lausanne
GfellerLabOther members
Selected Publications
Semi-supervised integration of single-cell transcriptomics data.
Andreatta M, Hérault L, Gueguen P, (...), Gfeller D, Berenstein AJ, Carmona SJ
Nature communications – 2024 Jan 29
Machine learning predictions of MHC-II specificities reveal alternative binding mode of class II epitopes.
Racle J, Guillaume P, Schmidt J, (...), Bassani-Sternberg M, Harari A, Gfeller D
Immunity – 2023 Mar 30
Contemplating immunopeptidomes to better predict them
Gfeller D, Liu Y, Racle J
Seminars in Immunology – 2023 Mar 1
Improved predictions of antigen presentation and TCR recognition with MixMHCpred2.2 and PRIME2.0 reveal potent SARS-CoV-2 CD8(+) T-cell epitopes.
Gfeller D, Schmidt J, Croce G, (...), Cesbron J, Racle J, Harari A
Cell systems – 2023 Jan 4
The MHC Motif Atlas: a database of MHC binding specificities and ligands.
Tadros DM, Eggenschwiler S, Racle J, Gfeller D
Nucleic acids research – 2022 Nov 1
Metacells untangle large and complex single-cell transcriptome networks.
Bilous M, Tran L, Cianciaruso C, (...), Carmona SJ, Pittet MJ, Gfeller D
BMC bioinformatics – 2022 Aug 13
Related news
Events
AGORA Sustainability Day
Events

AGORA PRS | June 18th
Events

Les coulisses de la recherche | June 6th
Events

AGORA PRS | December 5th
Events
Ludwig Distinguished Lecture, Prof. Sohrab Shah | September 14th
Events

AGORA PRS | May 23rd
Events











